Powertrain¶
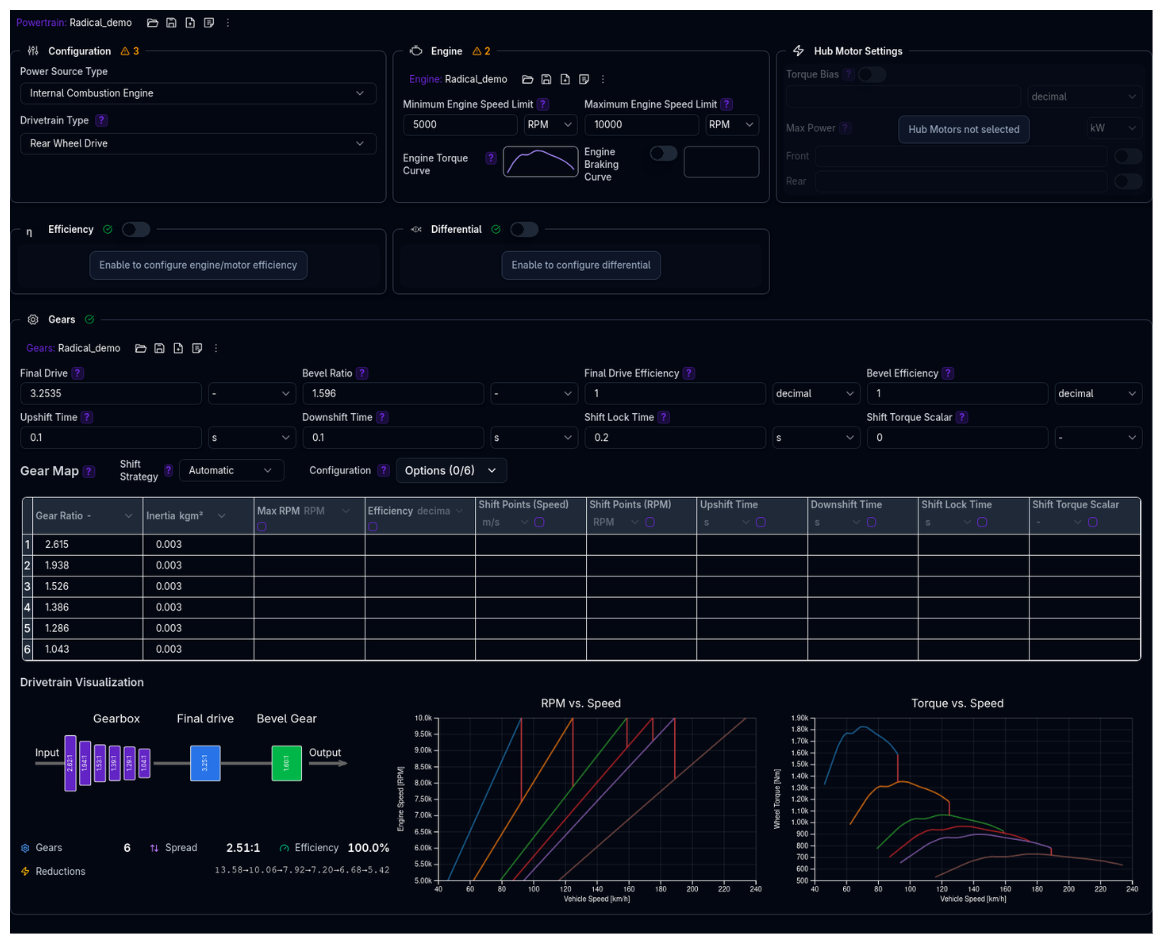
The Powertrain page configures your vehicle's power generation, transmission, and drivetrain systems. The powertrain is modular — subsystems are conditionally shown or hidden based on your power source type and optional feature toggles.
Component Structure¶
The powertrain is a parent component that references up to six child components. Each child is an independent library item that can be saved, loaded, and shared separately.
graph TD
PT["<b>Powertrain</b><br/><i>Power Source Type + Drivetrain Type</i>"]
ENG["<b>Engine</b><br/><i>Torque curve, RPM limits</i>"]
MOT["<b>Electric Motor</b><br/><i>Torque curve, RPM limits</i>"]
BAT["<b>Battery</b><br/><i>Cell config, voltage maps</i>"]
GRS["<b>Gears</b><br/><i>Ratios, shift strategy</i>"]
EFF["<b>Efficiency</b><br/><i>Constant or 2D map</i>"]
DIF["<b>Differential</b><br/><i>Type, locking behaviour</i>"]
PT --> ENG
PT --> MOT
PT --> BAT
PT --> GRS
PT --> EFF
PT --> DIF
style PT fill:#6366f1,color:#fff
style ENG fill:#ef4444,color:#fff
style MOT fill:#10b981,color:#fff
style BAT fill:#10b981,color:#fff
style GRS fill:#f59e0b,color:#fff
style EFF fill:#8b5cf6,color:#fff
style DIF fill:#8b5cf6,color:#fffNot all components are active at the same time — which ones are available depends on your configuration:
| Component | ICE | EV (FWD/RWD) | EV (Hub Motors) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Engine | Yes | - | - |
| Electric Motor | - | Yes | Yes |
| Battery | - | Yes | Yes |
| Gears | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Efficiency | Optional | Optional | Optional |
| Differential | Optional | Optional | Optional |
Page Layout¶
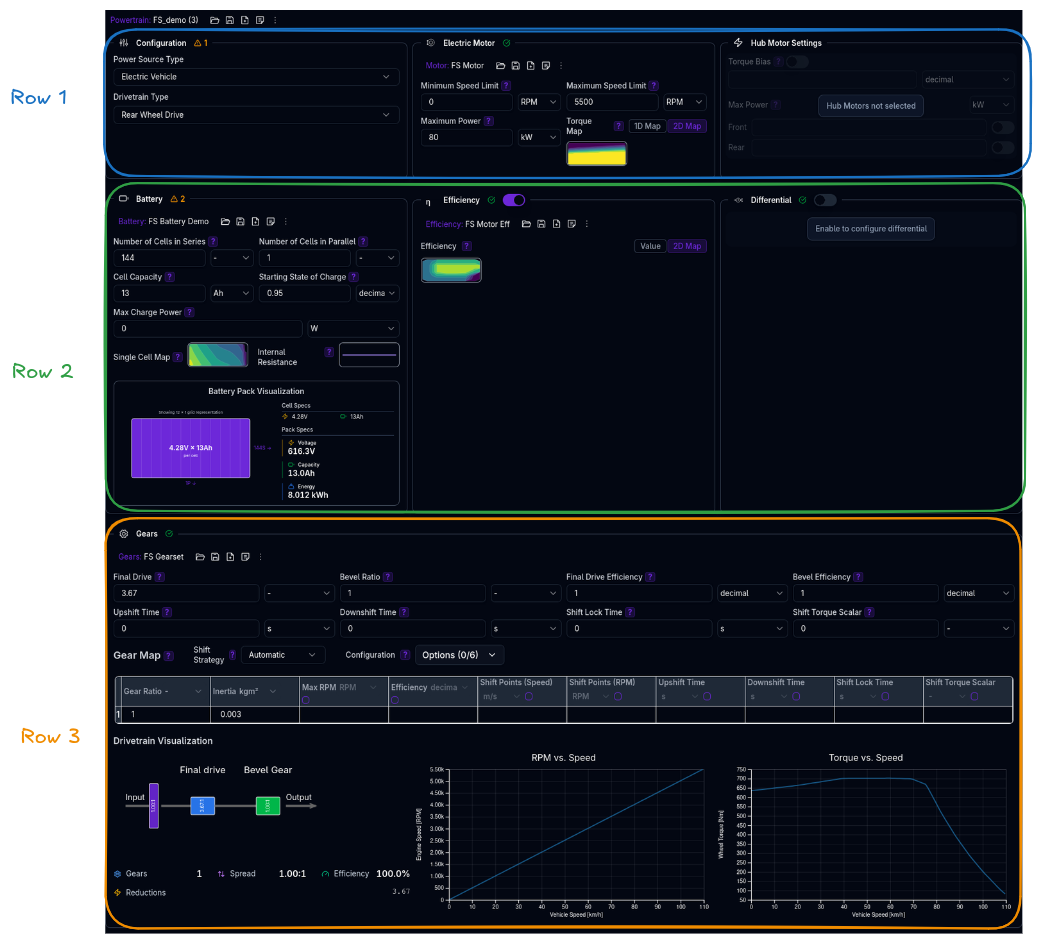
The Powertrain page is arranged in three rows:
Row 1 — Top: Three columns
- Configuration — Power source type, drivetrain type
- Engine (ICE) or Electric Motor (EV) — Power plant settings
- Hub Motor Settings — Only active when drivetrain is Hub Motors
Row 2 — Middle: Three columns
- Battery (EV only) — Cell configuration and voltage maps
- Efficiency (optional) — Engine/motor efficiency modelling
- Differential (optional) — Torque distribution behaviour
Row 3 — Bottom: Full width
- Gears — Ratios, shift timing, shift strategy, and visualisations
Configuration¶
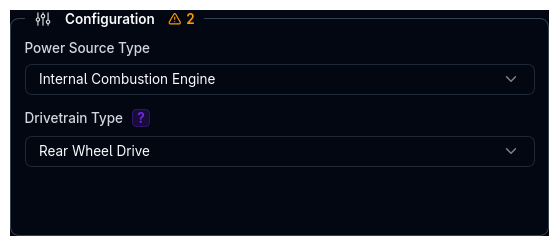
The Configuration fieldset contains the two primary selectors that determine the overall powertrain architecture.
Power Source Type¶
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) | Shows the Engine component. Hides Electric Motor and Battery. |
| Electric Vehicle (EV) | Shows the Electric Motor and Battery components. Hides Engine. |
Switching power source type automatically creates the required child components if they don't already exist.
ICE and Hub Motors
If you switch from EV to ICE while the drivetrain is set to Hub Motors, the drivetrain is automatically changed to Rear Wheel Drive (RWD), since Hub Motors require an electric power source.
Drivetrain Type¶
| Option | Description | Availability |
|---|---|---|
| Front Wheel Drive (FWD) | All drive torque goes to the front axle | ICE and EV |
| Rear Wheel Drive (RWD) | All drive torque goes to the rear axle | ICE and EV |
| AWD Hub Motors (HM) | Individual motors at each wheel with configurable torque bias | EV only |
Hub Motors and EV
Selecting Hub Motors automatically switches the power source type to EV if it isn't already.
Hub Motor Settings¶
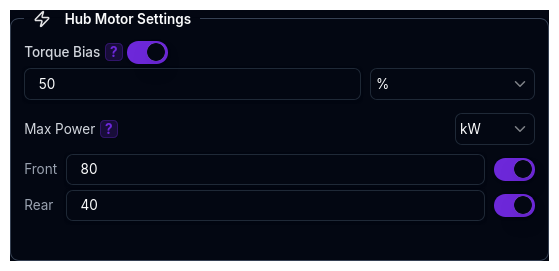
When the drivetrain is set to AWD Hub Motors, the Hub Motor Settings fieldset becomes active:
| Parameter | Description | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Torque Bias | Distribution between front and rear hub motors. 0 = all rear, 1 = all front, 0.5 = equal. | decimal (0–1) |
| Max Power | Maximum power limit per axle (front and rear independently). This is the total axle limit — for vehicles with 2 motors per axle, the limit is shared across both. | kW |
The Max Power field is optional. If not set, power is limited only by the motor torque curve.
Optional Components¶
Efficiency¶
The Efficiency component models drivetrain losses between the power source and the wheels. It is toggled on/off with a switch in the section header.
- When disabled, all drivetrain efficiency is assumed to be 100% (no losses)
- When enabled, the Efficiency component becomes available for configuration
See Efficiency for full details.
Differential¶
The Differential component models torque distribution behaviour between the driven wheels. It is toggled on/off with a switch in the section header.
- When disabled, an open differential is assumed
- When enabled, the Differential component becomes available for configuration
See Differential for full details.
How Torque is Calculated¶
The powertrain processes torque through a chain of components:
Power Source (Engine/Motor)
→ Base Torque at RPM
→ × Efficiency (if enabled)
→ × Gear Ratio × Final Drive × Bevel Ratio
→ Wheel Torque
→ ÷ Rolling Radius
→ Drive Force
→ Split by Drivetrain Type (FWD/RWD/HM)
Force Distribution¶
| Drivetrain | Front | Rear |
|---|---|---|
| FWD | 100% | 0% |
| RWD | 0% | 100% |
| Hub Motors | Torque Bias | 1 − Torque Bias |
Total Efficiency¶
The total efficiency applied to the base torque is the product of all efficiency stages:
Total Efficiency = Motor/Engine Efficiency × Gear Efficiency × Final Drive Efficiency × Bevel Efficiency
Each of these is configurable in the Gears and Efficiency components.
Validation Warnings¶
The powertrain validates the overall system configuration. Subsystem-specific warnings are documented on each component's page.
EV Source Warnings¶
| Condition | Warning |
|---|---|
| Motor max voltage > 95% of battery nominal voltage | Limited voltage headroom |
| Motor max voltage < 70% of battery nominal voltage | Possible efficiency loss |
| Power-to-energy ratio > 50 | Rapid battery depletion risk |
| Power-to-energy ratio < 5 | Oversized battery |
Subsystem Pages¶
- Engine — ICE torque curve, RPM limits, engine braking
- Electric Motor — Motor torque curve (1D or 2D), RPM limits, max power
- Battery — Cell configuration, voltage/discharge maps, internal resistance
- Gears — Gear ratios, shift timing, shift strategy, inertias
- Differential — Differential type, FACES inputs, locking behaviour
- Efficiency — Constant or RPM/torque-dependent efficiency