Differential¶
The Differential component models torque distribution between driven wheels, affecting traction, stability, and handling. It is an optional component — enable it via the toggle in the Powertrain page.
When disabled, an open differential is assumed.
The Differential is an independent library component — it can be saved, loaded, duplicated, and shared separately from the parent Powertrain.
Differential Types¶
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Open | Allows wheels to rotate at different speeds with no torque transfer between them |
| Locked | Forces both wheels to rotate at the same speed (50/50 torque split) |
| LSD | Limited-slip differential with configurable locking behaviour based on torque and/or speed sensing |
Differential Selection
- Open: Smooth handling, no binding in corners, but poor traction when one wheel has low grip
- Locked: Maximum traction to both wheels, but causes binding on high-traction surfaces
- LSD: Adaptive — behaves like an open diff at low slip, progressively locks under higher slip
LSD Configuration¶
When LSD is selected, two independent sensing modes can be enabled via toggles. You can enable one or both simultaneously — their locking contributions are additive.
Torque Sensing¶
Responds to torque differences between output shafts. When enabled, a torque map editor opens with three input methods:
User-Defined Formula (FACES)¶
Uses geometric parameters to calculate a torque map:
| Parameter | Description | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Power Ramp Angle | Ramp angle controlling progressive locking during acceleration | degrees |
| Brake Ramp Angle | Ramp angle controlling locking during deceleration | degrees |
| Max Faces | Maximum number of contact faces in differential mechanism | count |
| Actual Faces | Current number of active contact faces | count |
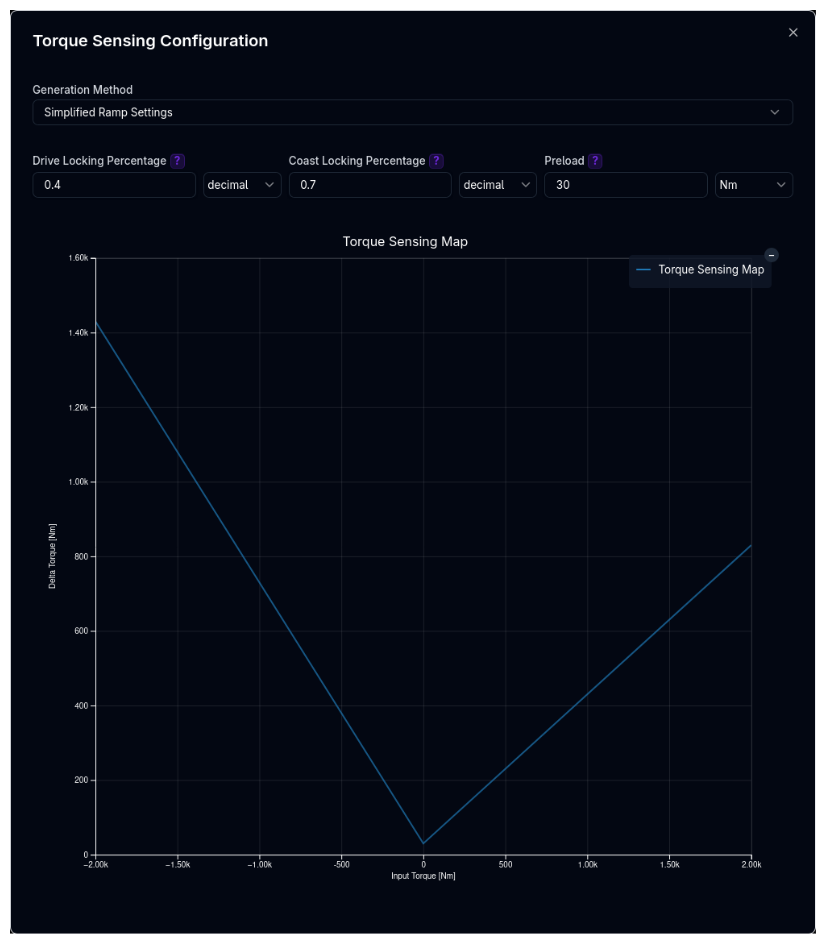
Simplified Ramp Settings¶
Direct locking control:
| Parameter | Description | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Drive Locking | Locking ratio during acceleration | decimal (0–1) |
| Coast Locking | Locking ratio during deceleration | decimal (0–1) |
| Preload | Constant torque always applied to differential | N·m |
Table Input¶
Custom torque map for advanced modelling — define the relationship between input torque difference and delta torque transferred.
All three methods generate a 1D torque map (input torque vs. delta torque) that the simulation uses at runtime.
Speed Sensing¶
Responds to speed differences between wheels (viscous LSD behaviour). When enabled, a 1D map editor appears:
- X-Axis: Speed difference between wheels (RPM)
- Y-Axis: Locking torque (N·m)
See Data Types for details on map editors.
Validation Warnings¶
| Condition | Warning |
|---|---|
| LSD selected with no speed or torque map provided | LSD differential is selected, but no speed or torque map is provided |
Tips¶
- Match to application: Open for street, LSD for performance, Locked for off-road or drag racing
- Use FACES for clutch-type LSDs: The formula models mechanical clutch-pack behaviour with power and coast ramp angles
- Use speed sensing for viscous LSDs: Viscous and helical designs respond to speed differences rather than torque differences
- Combine both modes: Enable torque and speed sensing together for more complex differential behaviour
Next Steps¶
- Configure Efficiency for complete powertrain losses
- Set up Gears to work with differential characteristics
- Return to Powertrain Overview